
In order to unwind DNA, these interactions between base pairs must be broken. Adenine only pairs with thymine and cytosine only binds with guanine.

DNA has four bases called adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) that form pairs between the two strands. DNA forms copies of itself by replication and codes for mRNA by transcription-the mRNA codes for the subsequent protein synthesis by translation.Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands. The proteins are responsible for conferring characters. It states that genetic information starts flowing from DNA to RNA and then to protein. The central dogma of Molecular Biology given by Francis Crick forms the foundation for genetic studies. The two chains are coiled in a right-handed fashion with 10 base pairs in each turn. If one strand has 5′ to 3′ polarity, the other has 3′ to 5′ polarity. The two chains of DNA have antiparallel polarity. In this way, a purine is always bonded to pyrimidine, so the distance between the two strands remains almost constant. Guanine is bonded to cytosine via 3 hydrogen bonds. Adenine is always bound to thymine via 2 hydrogen bonds. RNA is single-stranded and there is no base pairing.ĭNA is double-stranded and base pairing between particular nitrogenous bases of two different strands takes place. The nitrogenous bases are of two types- purine(adenine and guanine)and pyrimidine (cytosine and thymine in DNA and uracil in case of RNA).
#Summarize the process of dna replication free#
The polynucleotide chain will do have a free phosphate at the 5′ end and a free hydroxyl group of sugar at the 3′ end. Two adjacent nucleotides are bonded together by 3′-5′ phosphodiester linkage. The nucleoside is linked to a phosphate group. The nitrogenous base is bonded to the pentose sugar by an N-glycosidic linkage to form a nucleoside. The nitrogenous bases protrude outside.ĭNA is a polymer of nucleotides each nucleotide is made up of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar( ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in case of DNA) and a phosphate group. Watson and Crick described the molecular structure of DNA.ĭNA has a double-stranded helical structure with a backbone made of sugar and phosphate. Thus DNA replication is a form of semi-conservative replication because each DNA has one strand belonging to the parent and one new strand. These new strands of DNA are read by internal cell systems to check for errors and are stabilized to form new DNA. Once the DNA synthesis is finished, the lagging strand’s fragments are joined by the enzyme DNA ligase. This extension of new DNA strands continues until there is no more template to copy.

These fragments are known as Okazaki fragments and later joined. So the DNA primer synthesizes an RNA primer for every 200 nucleotides and the strand is copied downwards (5′ to 3′) in fragments. The other strand, which is in the direction of 5′ to 3′, the primer can’t be extended similarly as DNA polymerase acts in only one direction.
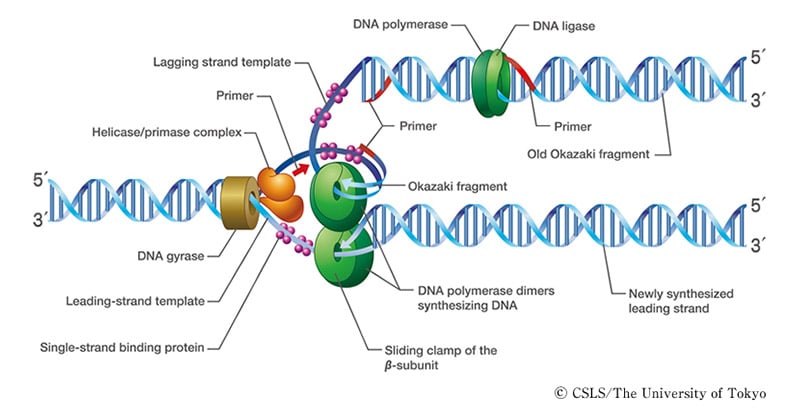
In this strand, the template is read from the 3′ to 5′ direction, and this is called the leading strand. The DNA polymerase attaches to the unwound strands of DNA, but this enzyme can only extend the primer from 5′ to 3′. Hence, only small parts of it are opened each time and replicated.ĭNA is extended by adding a free nucleotide triphosphate to the 3′ end of the chain.ĭNA replication can occur only in one direction (but remember, these two strands are antiparallel).Īnother enzyme called DNA Primase codes for a small RNA primer, which facilitates the activity of DNA polymerase. It is energetically expensive to unwind the entire length of DNA. So each exposed strand acts as a template for replication. This ATP forms the bonds between the base pairs (thus breaking the bonds). This is known as the replication fork and here, the process of replication begins.Īn enzyme DNA helicase unwinds the two strands by hydrolyzing the ATP. Around this origin point, a protein complex of initiator proteins is formed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
